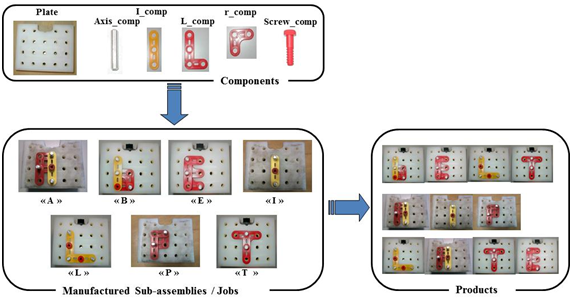
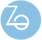
Components
Six components are available (“Plate”, “Axis_comp”, “I_comp”, “L_comp”, “r_comp” and “screw_comp”).
Purchase orders are assumed to insure sufficient quantities of these components as desired. In future research, a limited supply will be considered as a new constraint.
Jobs
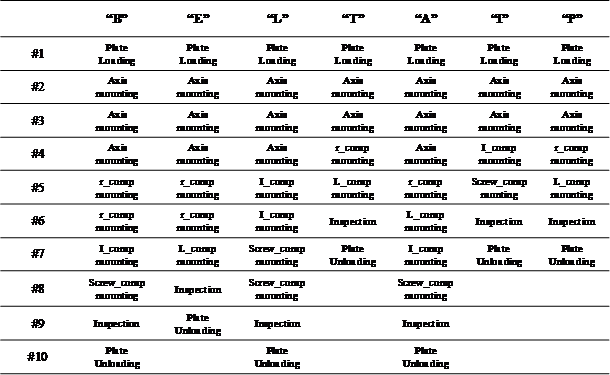
Seven types of jobs (sub-assemblies) can be manufactured. They are denoted “B”, “E”, “L”, “T”, “A”, “I” and “P”. Components are used to manufacture these types of job.
Production sequence
A manufacturing operation is an elementary action carried out on sub-assemblies, which is not a transportation task. There are eight manufacturing operation types (“Plate loading”, “Axis mounting”, “r_comp mounting”, “I_comp mounting”, “L_comp mounting”, Screw_comp mounting”, “Inspection”, and “Plate unloading”). For example, “I_comp mounting” means that the I component must be mounted on the plate. The inspection is completed by an automatic inspection unit (i.e., vision system).
A production sequence (ordered manufacturing operation list) is associated to each type of job. The operation lists have the same structure: a single load, a series of component mountings, a single inspection and a single unloading. Between two successive manufacturing operations, it may be required a transportation operation if the two operations are not done at the same place. Constraints 6 and 7 insure this relationship in the MILP.
Products and client orders
Three kinds of products are proposed to clients. They are called “BELT” “AIP” and “LATE”. A product is thus a subset of jobs, or sub-assemblies, among the seven possible job types, corresponding to different arrangements of letters. The jobs that compose these products can be manufactured in any order.